Cracow archaeologists have discovered a settlement from the Neolithic period in Jordan
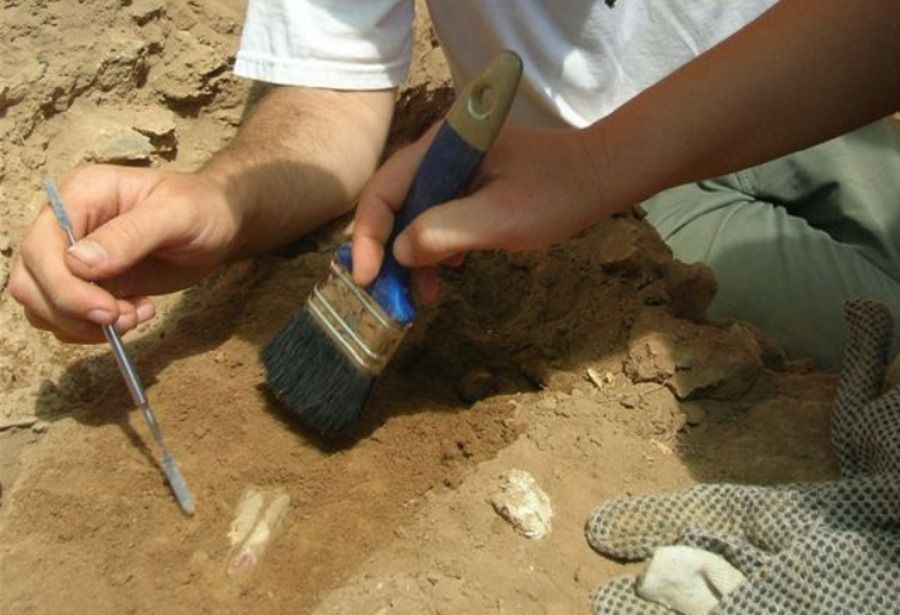
A settlement from the Neolithic period was discovered in southern Jordan by archaeologists from the Jagiellonian University in Cracow, Poland. They made the find in an inaccessible mountainous area where no one had done research before.
– Munqata’a is the easternmostod settlement associated with poThe most important phase of the Neolithic that has been discovered so far. Our research can be considered pioneering, as no one had previously excavated in this inaccessible gorian terrain – explained expedition leader Piotr Kolodziejczyk.
In his opinion, other momentous finds can be expected at the site. – We intend to probe more in the coming years – announced.
Discovered settlement from the timeoIn the Neolithic it had stone walls and a central building – probably a temple or chief’s house. Wokowallon Wok archaeologists have found many monumentsoin economic, such as grinders, quern stones, arrowheads, as well as a huge amount of pottery – vessels probably for storing suppliesoin food.
Getting to gorska valley, in whichorej made the discovery, was for the archaeologistow not only a scientific challenge, but also a logistical one. Descent to it is possible only by a steep path along a ridge of several hundred meters. With it, equipment and supplies of food and water had to be abolished.
Archaeologists, on the basis of geological and natural studies, assume that there was well-developed pastoralism in the valley, and the first crops were grown on the flatlands between the rocks.
Scientists from Krakow have been conducting research at the Munqata site since last year’a and the other in that area – Faysaliyya site, in the desert near the village of Shawbak. The site includes a settlement and economic complex. Archaeologists unearthed here m.in. stone walls surrounding a considerable sizeointo a homestead with farm and living quarters. Elsewhere, stone constructions related to the period of the so-called. Copper Age (Chalcolithic). Dating of these structures was possible thanks to finds of ceramic vessels, stone and flint tools.
The project will continue in the following years. Scientists want to make the first comprehensive proto determine the stageoin the functioning and importance of the South Jordan area between 3700 and 1950 p.n.e.
– It was an extremely interesting time in the Middle East, as civilization was born in these areas, agriculture and craft production technologies were developed, long-distance trade flourished, the first urban-like centers were established and a whole range of elementsoin cultures, whichore we know from today’s world. Between Egypt Pharaohoin and Mesopotamia SumeroThe site was located in what is now Jordan, which is today a white spot when it comes to research of this period – described by Piotr Kolodziejczyk.
Scientists’ projectow from the UJ is funded by a grant from the National Science Center awarded for 2017-2021. Employees, doctoral students and students take part in mandatory internships.